[bearing knowledge] type and positioning method of bearing bush
The bearing bush should have a certain strength and stiffness, be reliably positioned in the bearing, be easy to input lubricant, be easy to dissipate heat, and be easy to assemble, disassemble and adjust.

Fig. 1 bearing bush
1、 Type of bearing bush
The type of bearing bush can be classified according to structure, size, material and processing. China bearing network shares the following according to specific understanding:
1. Bearing shells are classified by structure
According to the structure, the bearing bush can be divided into integral bearing bush and split bearing bush.
1) Integral bearing bush

Fig. 2 integral shaft sleeve
This type of bearing bush needs to be installed and removed from the shaft end, and its maintainability is poor.
2) Split bearing bush
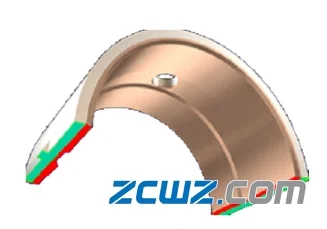
Fig. 3 split bearing bush
The split bearing bush can be directly installed and removed from the middle of the shaft and can be repaired.
2. Bearing shells are classified by size
Bearing shells can be divided into thin wall bearing shells and thick wall bearing shells according to size.
1) Thin wall bearing bush

Figure 4 thin wall bearing bush
This kind of Thin-walled bearing shell saves materials, but its stiffness is insufficient, so it requires high machining accuracy of bearing seat hole.
2) Thick wall bearing bush

Fig. 5 thick wall bearing bush
The thick wall bearing bush has sufficient strength and stiffness, which can reduce the machining accuracy requirements of the bearing seat hole.
3. Bearing bush is classified by material
Bearing shells can be divided into single material bearing shells and multi material bearing shells according to materials.
1) Single material bearing bush

图6 单一材料的轴瓦
这种单材料轴瓦的强度足够的材料可以直接作成轴瓦,如黄铜,灰铸铁。
2)多材料轴瓦
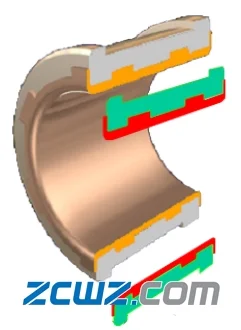
图7 两种材料的轴瓦
这种多材料的轴瓦衬强度不足,故采用多材料制作轴瓦。
4、轴瓦按加工分类
轴瓦按照加工方式可以分为铸造轴瓦和轧制轴瓦。
1)铸造轴瓦

Figure 8 cast bearing bush
The casting technology of this kind of cast bearing bush is good, and it can be produced in single piece and in large quantities. It is suitable for thick wall bearing bush.
2) Rolled bearing bush

Figure 9 rolling shaft sleeve
This kind of rolled bearing bush is only suitable for thin-wall bearing bush, with high productivity.
2、 Positioning method of bearing bush
1. Bearing bush positioning purpose
Prevent the axial and circumferential relative movement between the bearing bush and the bearing seat.
2. Axial positioning
Axial positioning can be divided into two cases, one is flange positioning (one or both ends of the bearing bush are flanges), and the other is lug (positioning lip) positioning.
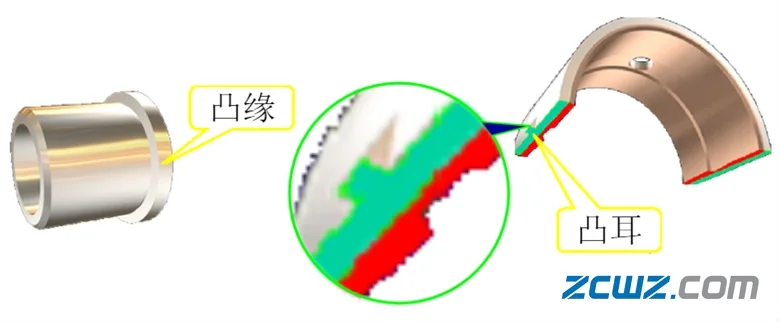
Figure 10 axial positioning
3. Circumferential positioning
Circumferential positioning includes the fixing of set screws and pins.
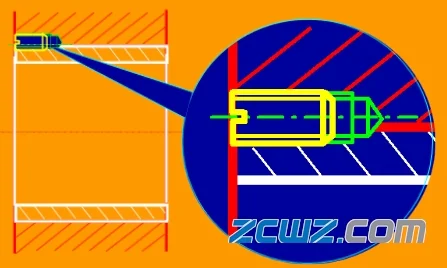
Fig. 11 fixing bearing bush with set screw
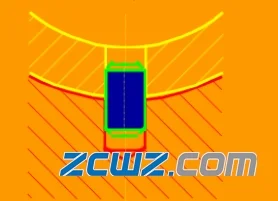
Figure 12 pin fixed bearing bush
3、 Oil hole and oil groove of bearing bush
1. Function: guide the lubricating oil into the journal and the moving pair surface formed by it.
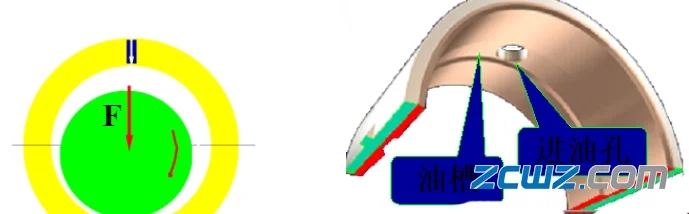
2. Opening principle
1) Try to open it in the non bearing area, and try not to reduce or reduce the bearing capacity of the oil film in the bearing area.
2) The axial oil groove cannot be opened to the end of the bearing, and an appropriate oil cover should be left.
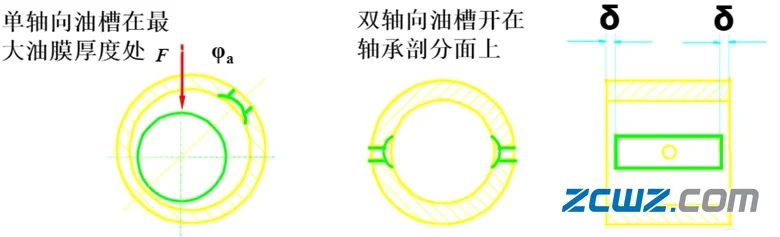
3. Form:
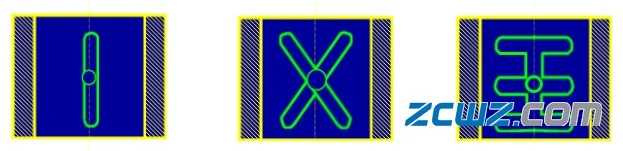
1) According to the direction of the oil groove - along the axial direction, around the circumferential direction, oblique direction, spiral line, etc.
2) The bearing midsection is often arranged perpendicular or nearly perpendicular to the load.
3) Large liquid sliding bearings are often designed to supply oil on both sides, which is conducive to the formation of dynamic pressure oil film and cooling effect.
When the load is inclined, the structure is shown in the figure:
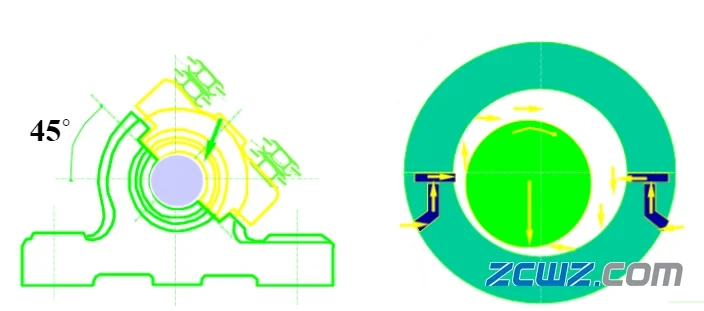
Important parameters (as shown in the figure):
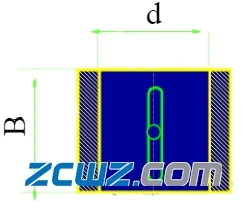
Note:
Width diameter ratio b/d --- the ratio of bearing bush width to shaft diameter.
Liquid lubricated friction sliding bearing: b/d=0.5~1.
Non liquid lubricated friction plain bearing: b/d=0.8~1.5.
- Prev:没有了!
- Next:没有了!


